On 5 October, a Russian Iskander short-range precision-guided ballistic missile struck a cafe in the village of Hroza 35 km away from the frontline, killing 52 people who gathered to commemorate a fallen soldier.
On 9 September, two volunteers, Emma Igual of Spain and Anthony Ignat of Canada, were killed, and two more were hospitalized when their car was struck by Russian shelling while assessing the needs of civilians caught in the daily crossfire.
What connects these tragedies is the fact that the weapons used were built using Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machine tools, produced in the West and imported into Russia. Shockingly, despite sanctions, Russia continues to buy high-precision machine tools and spare parts from Western firms, enabling it to commit the most atrocious war crimes.
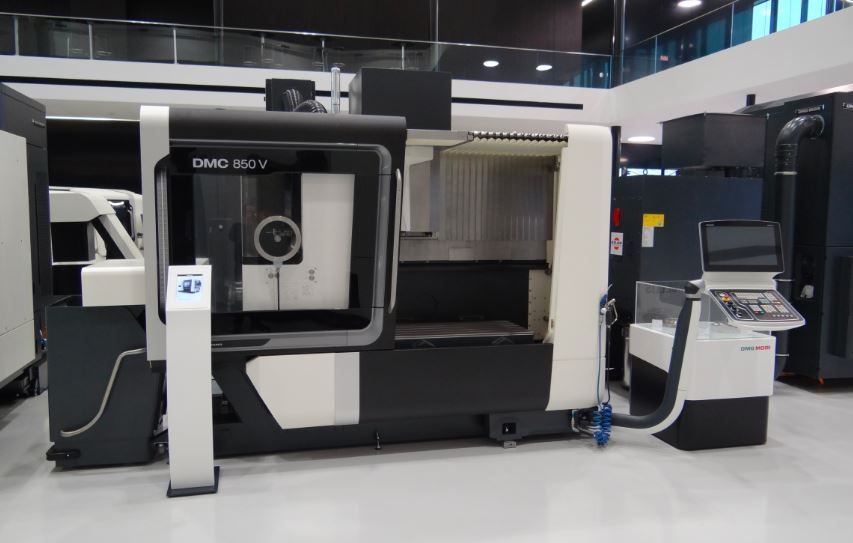
Example of a CNC. Produced by the Japanese-German multinational company DMC, the DMC 850 V Vertical Machining Center is a highly advanced, computer-controlled carving tool that can precisely shape a block of metal into parts essential for Russia’s military complex. Photo: Wikimedia Commons
At least 70% of all Russian CNC machine tools are imported, largely from the US, EU, and Japan. Over 80% of all CNCs end up in Russia’s military production facilities.
This makes CNCs a perfect target for the West to degrade the Russian military complex by clamping down on imports. Researchers from the Economic Security Council of Ukraine (ESCU) have recently developed a roadmap to achieve just that.
What are CNC machine tools?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tools are automated robot machines using software to manufacture various metal products without direct human intervention. CNC machinery is a crucial means of production for advanced arms manufacturing such as missiles, aircraft, or radars.
WСNC machines are the backbone of Russia’s military production and a window of opportunity for trying to stop the aggressor, ESCU said.
With a CNC, a computer program does all the necessary shaping and cutting. The machine tool uses a drill bit mounted on a head that moves in three dimensions to automatically carve digitally modeled shapes into metal.
Mechanical technician operative of a CNC milling cutting machine center at a tool workshop. Credit: Depositphotos
What can CNC machines produce?
There is not a single Russian tank, plane, or APC that does not have parts made with foreign CNC machine tools. Even nuclear weapons are manufactured with the help of CNC machinery. With the help of CNCs, Russia produces:
• Aircraft components: engine components, landing gear parts, and structural elements.
• Weapon systems: firearm components, missile guidance systems, and other weapon parts.
• Armor and vehicle components: body panels, turrets, etc;
• Electronic and communication equipment: communication equipment, and radar systems for military use.
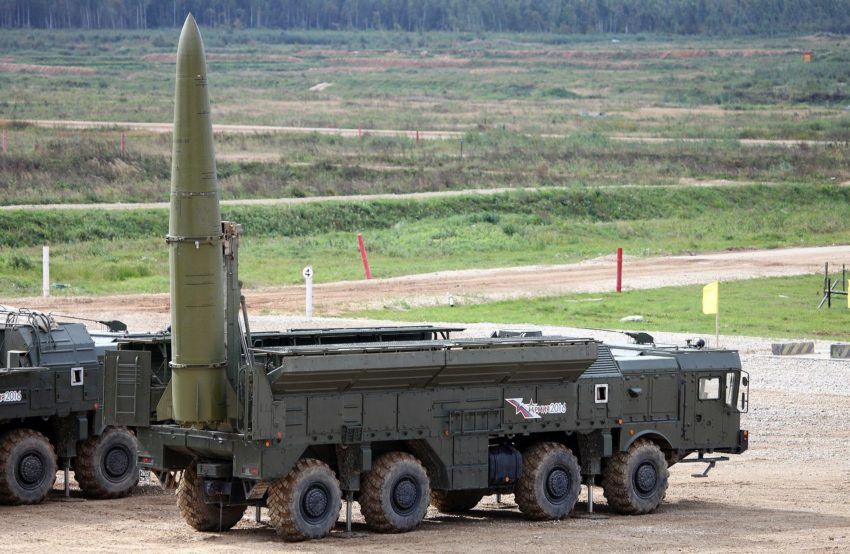
Russia would not be able to produce this Iskander missile if the West blocked CNCs with which it builds such weapons. Source: Wikipedia
Why are CNCs crucial for the Russian military production process?
Western CNC machine tools are irreplaceable. According to the annual World Machine Tool Survey conducted by Gardner Business Media, Russia was one of the top 10 importers of machine tools in 2022.
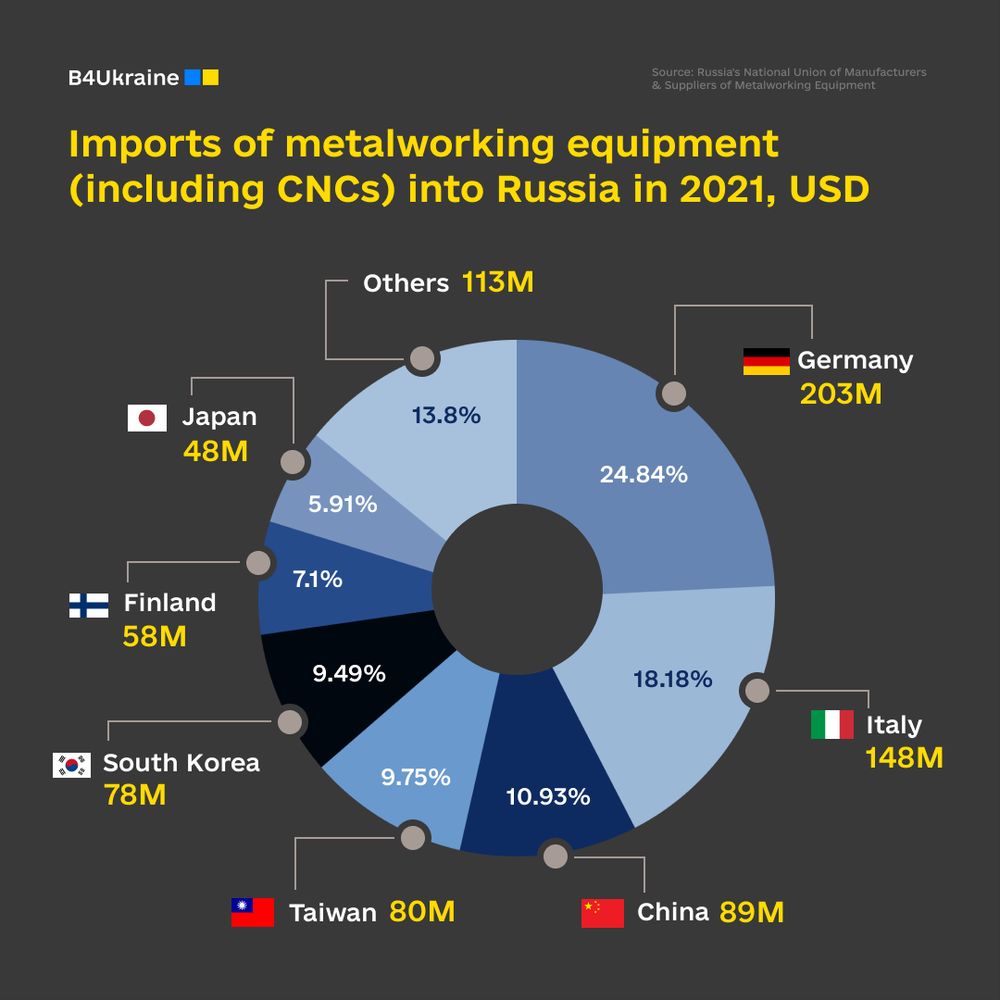
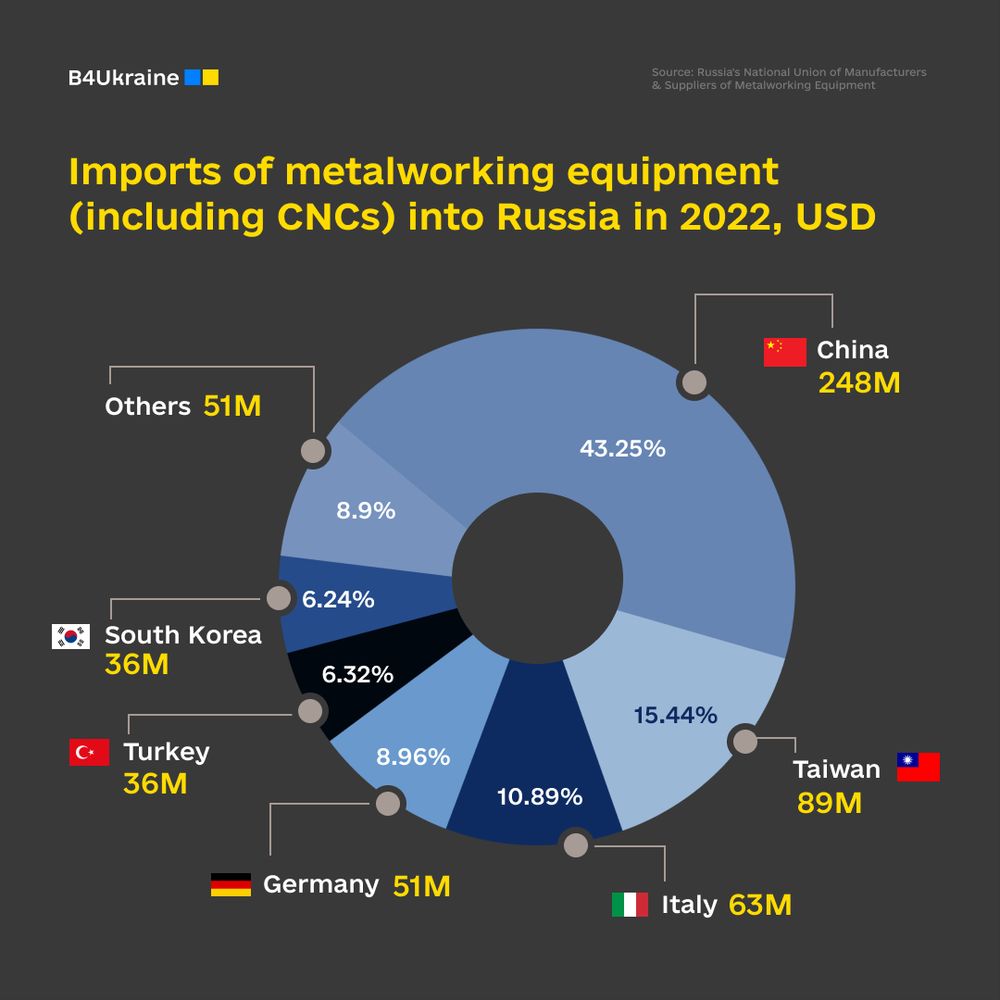
The absence of precision machine tool manufacturing at home makes Russia dependent on Western-made CNCs. Subject matter experts estimate that at least 70% of all Russian CNC machine tools are imported, and more than 80% of all CNCs end up in the military production facilities of the aggressor state.
While China remains a global leader in providing Russia with CNC machinery, Germany is a frontrunner in Europe, with at least $242 million worth of tools supplied to the aggressor state since the start of the full-scale invasion.
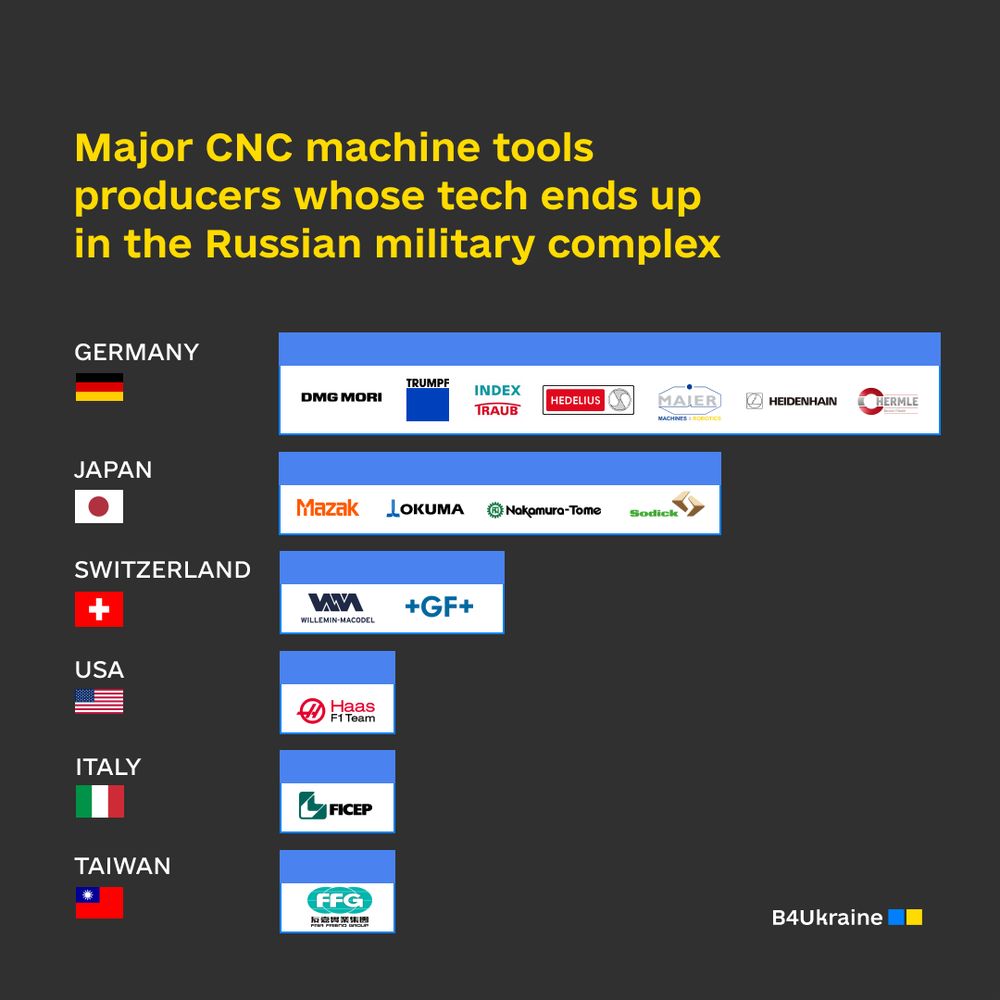
Major producers of CNCs used by Russia
The most influential manufacturers are DMG Mori, Trumpf, Fair Friend Group, Haas, Sodick, Dr. Johannes Heidenhain GmbH, Maier Werkzeugmaschinen GmbH & Co., KG HEDELIUS, GF Machining Solutions, Yamazaki Mazak Corporation, Okuma, Index Traub, Hermle, FICEP, Nakamura-Tome, Willemin-Macodel.
Japan and Germany are the top two CNC producers whose machines help Russia produce high-tech weapons.
Examples of Western CNC machine tools ending up in the Russian military complex despite sanctions
According to an investigation by PBS, USA company Haas was indirectly supplying the Russian arms industry. The firm denied any allegations and said it halted sales when Russia invaded Ukraine in 2022.
Dozens of German, Swiss, and Italian firms are formalizing deals with the Russian defense industry through shell companies and circumventing sanctions imposed in 2014, according to InformNapalm. PBS reported that a German-American manufacturer Niles-Simmons sends CNC machine tools to Russia to build weapons.
A breaking news story from Germany’s weekly Die Zeit has highlighted the role of a German engineering company DMG Mori in fueling Russia’s military production.
According to Germany’s news agency RND, the tech of another German CNC machine tool producer, NSH-Gruppe, also continues flowing to Russia.
How CNC exports to Russia could be blocked
Sanctions should become an effective economic weapon in time of war, not simply a deterrent. After almost two years since Russia’s invasion, it is clear that a more targeted and coordinated approach is crucial to degrade the Russian war machine.
According to Bloomberg, Russia now makes more money from oil revenues than before the invasion. Consequently, it faces no issues with increasing war financing to record levels, with 2024 military expenditures set to increase from 6.4 to 10.8 trillion rubles.
In the first half of 2023, Russia imported almost $800 million worth of high-priority battlefield technology, despite export controls on Western technology, according to the Atlantic Council’s Russia Sanctions Database.
Targeting the CNC machines sector is a cost-effective way to significantly weaken Russia’s weapon production capabilities. This can be achieved by following a set of recommendations developed by the ESCU researchers:
• Western allies have to expand export controls to CNC machine tools and spare parts. Currently, only the most sophisticated CNCs are subject to controls, and many components and upgrade kits are not banned;
• Implement sanctions on intermediaries and shell companies systematically and regularly to limit the opportunity for evasion;
• Introduce smarter compliance regulations. This means that CNC producers need to thoroughly check potential clients, with a risk-based approach, the risk being that the technology ends up in the wrong hands. Currently, producers only check sanctions lists and work freely with distributors;).
• Compel producers of CNCs to go through the Know-Your-Customer compliance practice to check (potential) clients in terms of various risks and introduce severe penalties for violations.
• Make producers install GPS trackers on CNC machine tools, stop servicing and providing software updates to all CNCs sold or used in Russia.
The report’s key findings have already been presented to the US Congressmen and law enforcement agencies. More than 20 US congressmen have written a letter of concern to Mr Sullivan, the US National Security Advisor, calling upon the National Security Council to make CNC machinery a priority of its sanctions policy.
By denying access to modern manufacturing tools, Western allies can use a cost-effective way to ensure that Moscow is unable to sustain its current military production levels and, therefore, is more likely to lose in its ongoing war of attrition against Ukraine.