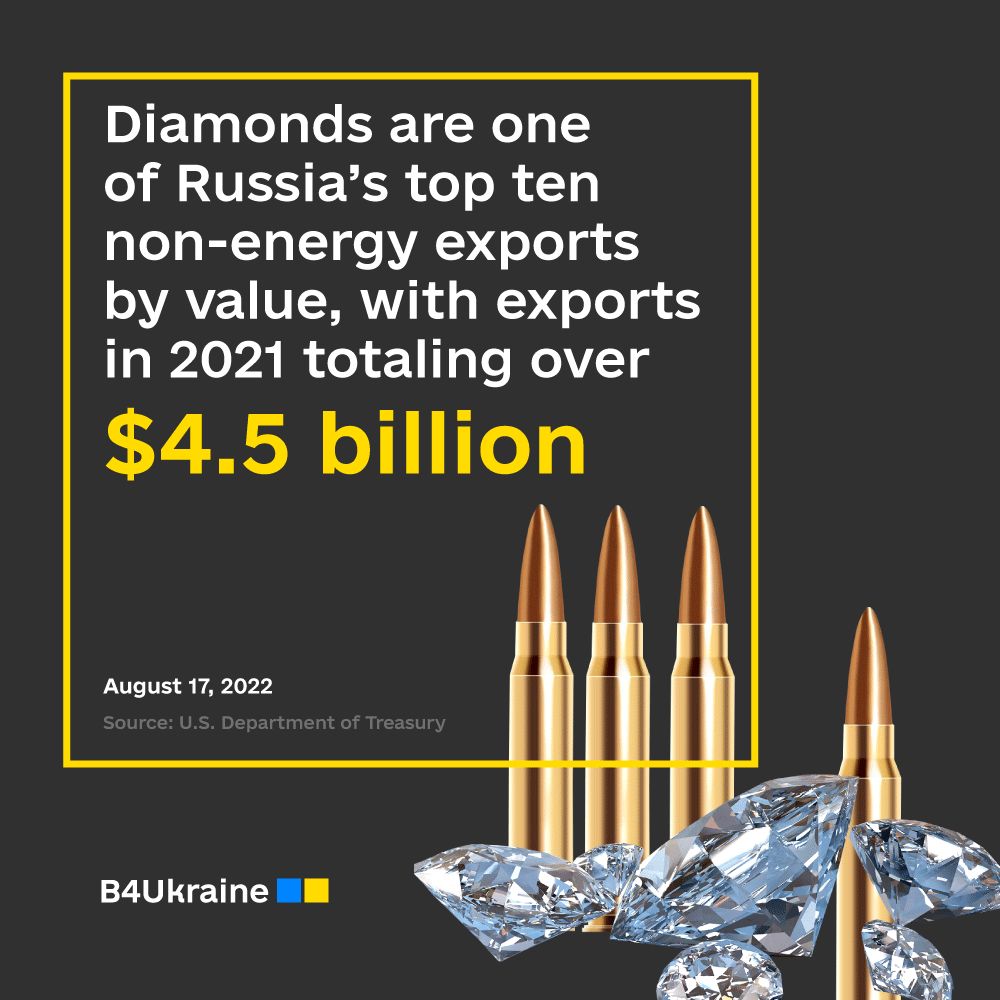
The export of diamonds is one of Russia’s primary sources of funding for the unprovoked war against Ukraine and should be eliminated. According to the U. S. Treasury data, diamonds are one of Russia’s top ten non-energy exports by value, with exports in 2021 totaling over $4.5 billion. The world’s largest diamond mining company, accounting for 28% of global diamond mining, is a Russian company Alrosa, which is majority-owned by the Russian federal and regional governments.
The reason behind the success of Russian diamonds is that they have been an alternative to African blood diamonds. The U.N defines blood diamond as a precious stone mined in areas controlled by forces opposed to the legitimate, internationally recognized government of a country and that is sold to fund military action against that government. The Kimberley Process, created in the wake of diamonds financing a deadly war in Sierra Leone and elsewhere, defines them more specifically, as “rough diamonds used by rebel movements or their allies to finance conflict aimed at undermining legitimate governments.”
Although Russia is not a rebel movement but an aggressor country and a terrorist state, Russian precious stones that are in no way less bloody than African and their use is as unethical. Even industry giants such as Tiffany, Signet Jewelers, and Brilliant Earth has already refused to purchase Russian gems. And so, the definition of blood diamond needs to be reviewed to include precious stones sold for profits that can further be used to fund unjustified warfare against another state.
The need for a more comprehensive definition of blood diamonds also comes with the loopholes in the sanctions that still allow the Kremlin to benefit from the diamond trade.
The U.S. imposed sanctions on Russian diamond exports back in the spring of 2022, but they are applied only to rough diamonds, gems that were dug from the ground but had yet to be cut and shined. Most rough diamonds are shipped abroad for transformation, mostly to polishing centers in India. Once the diamonds are transformed and readied for shipping, their origin changes. So, diamonds mined in Russia are no longer Russian-origin diamonds; they’re labeled Indian-origin and then are exported to the U.S. and other countries, according to NY Times.